
Health Is Wealth
Hemp and Cannabis education demystifying the plant and promoting good health while breaking stigmas along the way.
Get Your Medical Marijuana Card
Health Is Wealth Forum

Monthly Webinar Series
M4MM's Health Is Wealth monthly webinar series is designed to meet the educational needs for healthcare professionals by ensuring they are provided resources and information about cannabis as a medical alternative for patients. Although we don’t include sections specific to professionals, much of this information will be useful for pharmacists, physicians, nurses, and social workers.

Do You Qualify As A Medical Patient?
M4MM Physician Network

Get your medical marijuana card online in minutes. How can cannabis help me?
Easily discover what and how medical marijuana can help you or a family member..
Join The M4MM Physician Network

The Plant: Cannabis as Medicine
The Science Behind Cannabis
Cannabinoids are a diverse set of chemical compounds that bind to special receptors in the human body that make up what is known as the endocannabinoid system. The “key and lock” metaphor is often used to describe this process. The human body possesses specific binding sites (“locks”) on the surface of many cell types, and our body produces several endocannabinoids (“keys”) that bind to these cannabinoid receptors (CB) to activate or “unlock” them.
In 1992, researchers detected an endogenous substance that binds to cannabinoid receptors for the first time. This substance, known as anandamide, comes from the Sanskrit word “Ananda” for bliss and “amide” due to its chemical structure. A second endocannabinoid was discovered in 1995, 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG). These two endocannabinoids are the best studied so far. Today, it is thought that about 200+ related substances exist, which resemble the endocannabinoids and complement their function in what has been termed the “entourage effect.” Several endocannabinoids do not only bind to cannabinoid receptors, but also to a possible CB3 receptor (the GPR55 receptor), to vanilloid receptors and further receptors.
In addition to endocannabinoids, scientists have now identified cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant (phytocannabinoids) that work to mimic or counteract the effects of some endocannabinoids. Phytocannabinoids and terpenes are manufactured in resin glands (trichomes) present on the flowers and main fan leaves of late-stage cannabis plants. The amount of resin produced and its cannabinoid content varies by plant gender, growing conditions and harvesting time. The chemical stability of cannabinoids in harvested plant material is affected by moisture, temperature, light and storage, but will degrade over time in any storage conditions.When a cannabinoid causes a receptor to act in the same way as it would to a naturally occurring hormone or neurotransmitter, then it is labeled “agonist.” On the other hand, if the cannabinoid prevents the receptor from binding to the naturally occurring compound, thereby causing the resulting event (e.g., pain, appetite, alertness) to be altered or diminished, it is labeled “antagonist.” Research is mounting to better understand how specific cannabinoids can unlock (or lock in some cases) specific receptors.
Over 100 phytocannabinoids have been identified in the cannabis plant, many of which have documented medicinal value. Most are closely related or differ by only a single chemical part. The most talked-about and researched cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant are tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) for its psychoactive properties (“high feeling”) and cannabidiol (CBD) for its healing properties.Cannabinoids can be administered by smoking, vaporizing, oral ingestion, transdermal patch, intravenous injection, sublingual absorption or rectal suppository.
Still Have Questions?
Endocannabinoid System
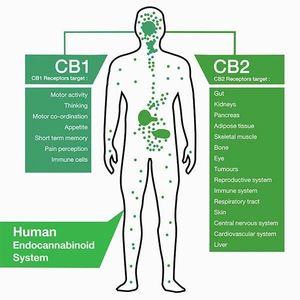
An Endogenous Cannabinoid System (ECS), commonly referred to as an “Endocannabinoid System,” is found in every animal and regulates a broad range of biological functions. The ECS is a biochemical control system of neuromodulatory lipids (molecules that include fats, waxes, sterols and fat-soluble vitamins such as vitamins A, D, E and K and others) and specialized receptors configured to accept certain cannabinoids. In general, a given receptor will accept only particular classes of compounds and will be unaffected by other compounds, just as a specific key is needed to open a lock.
Specialized receptors are located throughout the human body, including but not limited to, in the hippocampus (memory, learning), the cerebral cortex (decision-making, emotional behavior), the cerebellum (motor control, coordination), putamen (movement, learning), the hypothalamus (appetite, body temperature) and the amygdala (emotions).
The Entourage Effect

The theory is that cannabinoids within the cannabis plant work together through a network of coincidental relationships as part of a greater organism and affect the body in a mechanism similar to the body’s own endocannabinoid system. Basically, these compounds work better together than in isolation.
Research on the benefits of THC and CBD in isolation is well established. THC demonstrates analgesic, anti-emetic, and anti-inflammatory properties. CBD possesses anti-psychotic, anti-seizure, and anti-anxiety properties. However, evidence is mounting that by isolating these cannabinoids or creating them in a lab, that the resulting effects may have limited therapeutic use. It is also the reason visits to a doctor or emergency room have increased. When delivered in high concentrations, THC can cause overdosing. Although an acute THC overdose rarely requires medical intervention, the side effects can be very unpleasant. Good evidence now shows that THC and CBD work together. CBD is known to lock out THC at the CB1-R. Therefore, applying the entourage effect, increasing CBD in the case of an overdose may lessen the effects of THC.

Medical Cannabis Report
Effect of Inhaled Cannabis for Pain in Adults W/ Sickle Cell: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Frequently Asked Questions

Do I qualify As A Patient?
The passing of Medical Marijuana bills allows patients to obtain a medical marijuana card if they have a qualifying medical condition and a licensed physician believes they are likely to receive therapeutic or palliative benefit from the use of medical marijuana.
Some conditions to consider.
Cancer Glaucoma HIV/AIDS Sickle Cell Anemia Hepatitis C MLS Crohn’s disease Alzheimer’s disease Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
The treatment of these conditions; or a chronic or debilitating disease or medical condition or its treatment that produces one or more of the following: cachexia or wasting syndrome, severe and chronic pain, severe nausea, seizures (including but not limited to those characteristic of epilepsy), or severe and persistent muscle spasms (including but not limited to those characteristic of multiple sclerosis).
What is the difference between CBD vs. THC?
CBD is not an acronym it stands for cannabidiol the name of the entire group of chemical compounds also known as cannabinoids which can be found naturally in the cannabis and hemp plant. Cannabis plants contain THC the psychoactive chemical that provides the "high" or "euphoria effect". Many varieties of cannabis are grown for medical purposes specifically and are bred to have a high CBD and very low THC content. The THC acts as a driver for the CBD which is commonly known as the "entourage effect". Strains are created for specific medical conditions and when titrated just right will provide relief and immediate benefit for patients.
Does CBD have any side effects?
CBD is an anti-inflammatory agent. It is not the same as THC. CBD has no side affects or contraindications. CBD has no psychotropic affect. So whatever you are taking for various health and physical issues you do not have to worry about adverse drug interactions.
What is Hemp?
Hemp is a plant that happens to be the kissing cousin of the cannabis plant. A negligible amount of THC is contained in the hemp plant therefore, we don't recommend trying to smoke it Hemp has over 25,00 applications which include such things as dietary supplements, skin products, clothing, textile, and accessories.
Whats the difference between Indica and Sativa Cannabis plant?
There are three classes of the flowering Cannabis plant. Today we will discuss Cannabis Sativa vs. Cannabis Indica. Sativa tend to be rich in THC while Indica tend to be abundant in other cannabinoids. Indica strains generally provide a sense of deep body relaxation. Sativa strains tend to provide a more energizing experience. If you want a combination of the two in a variety of ways the strain is called a hybrid.
What is the best way to take medical Cannabis?
Inhalation is the fastest acting method to get the benefit from taking the medicine quickly. When inhaled, the active ingredients of Cannabis pass directly into the bloodstream from the lungs. Typically one can feel the effect between 5-20 minutes. Vaporizers are the preferred method for rapid relief of inhalation without the toxic and carcinogenic by-products of smoking.
Cannabis vs. CBD & Your Patients
Endocannabinoid Pharmacology: Patient & Consumer Safety
Health is Wellness: Meet The Cannabis Nurses of Color
Health is Wellness: Cannabis and Traumatic Brain Injuries
Copyright © 2026 Minorities for Medical Marijuana - All Rights Reserved.
This website uses cookies.
We use cookies to analyze website traffic and optimize your website experience. By accepting our use of cookies, your data will be aggregated with all other user data.
Are You 18 or Older?
Welcome to Minorities for Medical Marijuana. If you are 18 or older click below to learn more about our education, advocacy, training and resources.

